GST Full Detail
GST stands for Goods and Services Tax. In Hindi it is called Goods and Services Tax.
About GST
GST is a value added tax which is a single tax on the supply of goods and services from the manufacturer to the consumer.
GST is short for Goods and Services Tax. It is a comprehensive indirect tax system developed in India that eclipses all other forms of taxes. It is a multi-platform and destination-based tax system that has to be followed and is levied on a wide range of goods and services.
GST Full Detail
GST rates in India in 2023 are classified into four different GST slabs: 5%, 12%, 18%, and 28%. Goods and services are taxed at different rates depending on their nature, category and use.
What is the main objective of GST?
What is GST? GST is a form of indirect tax, similar to service tax or VAT indirect taxes. It aims to unify the Indian market and will act as a tax for the entire nation. GST will be applied on the supply of all goods and services from the manufacturer to the consumer.
GST Full Detail
When was GST implemented?
This tax came into effect from 1 July 2017 through the implementation of the One Hundred and First Amendment to the Constitution of India by the Government of India. 1st July is celebrated as GST Day. GST replaced many existing taxes imposed by the central and state governments.
Where was GST implemented first?
France is called the father of GST in the world because France was the first country in the world to implement Goods and Services Tax (GST). It had implemented GST in 1954 itself. Today more than 140 countries around the world have implemented GST.
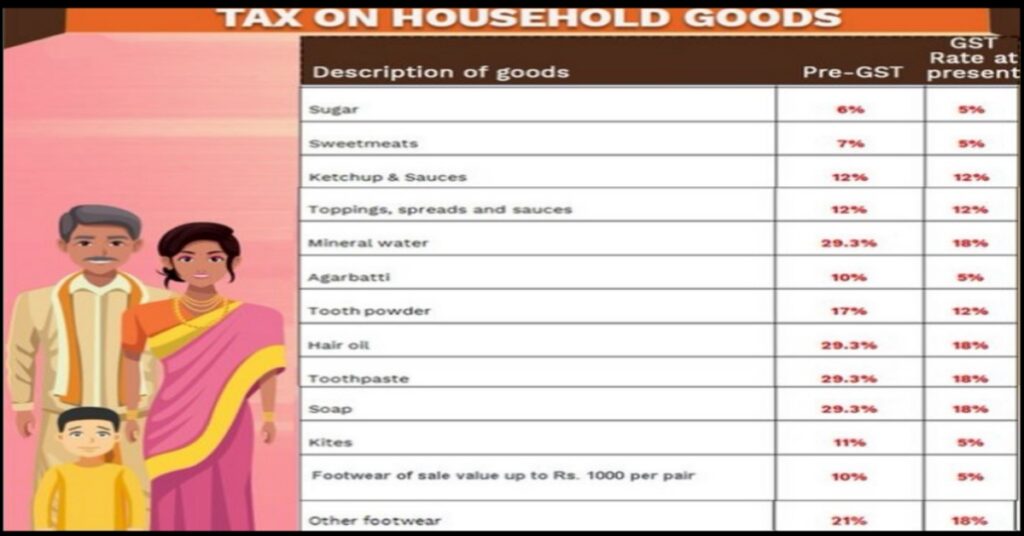

Where and how much is GST charged?
0% on sugar, egg, salt
5% on medicine
Computer Accessories 12%
18% for school bags
28% in any fantasy game
GST Full Detail
.
Related more information – GST a to z full detail
.
Who imposes GST?
In case of central sale, the Center has the right to impose tax, but this tax is collected by the states and retained by the states themselves. In case of services, only the Central Government has the right to levy service tax.
GST Full Detail
What is example of GST?
For example, a businessman in any one state sold goods to a consumer in that state for Rs 10,000. The GST rate is 18% which includes CGST rate of 9% (CGST means central gst) and SGST rate of 9% (SGST means state gst). In such cases the dealer deposits Rs 1800 and of this amount, Rs 900 will go to the Central Government and Rs 900 will go to the State Government.
Up to how many lakhs is GST free?
Your tax liability will be Rs 12,500 on income up to Rs 5 lakh, but Section 87A will be applicable here.
GST Full Detail
Why was GST brought?
The objective of GST is also to increase the taxpayer base by simplifying the process of taxation in India. GST has also given a boost to digitization of business. This has happened due to most of the tax filing being online under GST. The country’s treasury has also benefited greatly from GST and it has increased tax collection.
To formulate the GST rules, the Government has appointed a GST Council consisting of 33 members, which is chaired by the present Union Finance Minister………….
GST Full Detail
What happens if you don’t pay GST?
According to a BusinessLine report, if businessmen do not file their GST returns, their bank accounts may be seized or their registration may be cancelled. The Finance Ministry has put forward a part of the SoP regarding non-filing of GST returns.
How many types of GST are there
GST Full Detail
There are four types of GST
Integrated Goods and Services Tax (IGST)
State Goods and Services Tax (SGST)
Central Goods and Services Tax (CGST)
Union Territory Goods and Services Tax (UTGST)
1 Integrated Goods and Services Tax (IGST)
IGST means if any goods i.e. cloth from one state is sold in another state then IGST is levied on it. Suppose a cloth is manufactured in state A and the cloth is sold in another state i.e. state B, then IGST will be levied here. And if the cloth will be sold in another state i.e. B, the government there will collect GST.
I bought clothes and the GST charged on them, 18% or 15%, goes directly into the government’s account. Suppose 18 percent GST is levied on clothes, then 9 percent will be kept by the state and the remaining 9 percent will go to the central government.
Even if IGST is levied, the state government in which the cloth is sold will directly get 9 percent GST and the central government is sure to get 9 percent.
In IGST, if I sell a pen worth Rs 50 from my state to another state, then GST will be levied on that too. Similarly, if I sell an item to a friend for Rs 50,000, I will not have to pay GST. If I sell a good whose price is Rs 1000 in my state, then no GST will be charged. GST will be applicable on selling goods in my state when I do business of Rs 20 lakhs annually. Whereas if I sell goods in another state, even if my business is worth Rs 100, GST will be charged.
GST Full Detail
2 State Goods and Services Tax (SGST)
If my business is worth Rs 20 lakh, then GST will be levied on any item I sell in the state. Except some items like eggs, sugar etc. Suppose I sell clothes and there is 18 percent GST on it, then the state government will get 9 percent GST directly and the central government is sure to get 9 percent. I will pay GST only if my business is worth Rs 20 lakh. GST is not applicable on small businesses. GST is levied in business up to Rs 15 lakh but is waived off.
GST Full Detail
3 Central Goods and Services Tax (CGST)
No matter where I sell my goods in my state, CGST will be levied on it in other states. That means Central GST will be imposed. Suppose my shop is in some state, should I sell my goods in that state or in another state, GST will be charged on it. Suppose 18 percent GST is applicable on that item, then 18 percent will be divided into two equal parts. In 9-9 percent. 9 percent will go to the center which is called CGST. The state government will take 9 percent of the amount in which it is being sold.
GST Full Detail
4 Union Territory Goods and Services Tax (UTGST)
GST will be imposed here in Union Territories like Jammu, Delhi, UT. Here I am from Delhi. I have a shop in Delhi, I sell my goods in Delhi only. That means, if I sell in a Union Territory, the Central Government will not only take its GST, the Central Government will also take its GST. Suppose 18 percent GST is levied on any goods sold, then 9 percent will be taken by the Central Government and 9 percent will be taken by the Union Territory Government.
GST is different on all goods. But GST will be the same in any state or country. Suppose if a Vivo mobile has 18% discount in one state, then it will be 18% in another state also. It was not the same earlier. In one state it was 12 percent on a mobile and in another state it was 18 percent on the same mobile. Today everything is the same.
GST Full Detail
Read more >>
Vivo X100 Pro Latest Smartphone With Best Camera
Banking Industry Analysis Essay Topics
Finance Project Topics Idea For All
Research Topics For Finance 2024






